Project summary
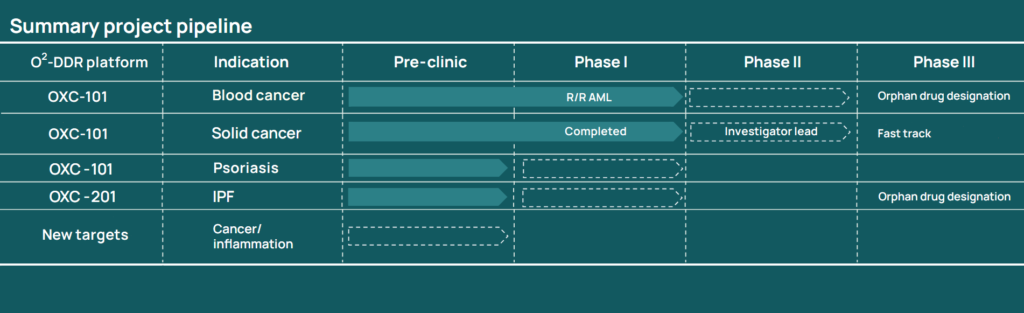
Oxcia currently has two small molecule drug candidates, both with potential to be first in class. OXC-101, a mitotic MTH1 inhibitor, is in late clinical phase 1 development in cancer patients with advanced solid cancer and blood cancers, it is also in pre-clinical development aimed at curing plaque psoriasis. OXC-201, an OGG1 inhibitor, is being developed to treat inflammatory and fibrosis-related diseases, with a focus on pulmonary fibrosis and is in the preclinical stage.
Oxcia develops unique and revolutionary treatments through the innovative use of oxidative DNA damage and DNA Damage Response (DDR) processes to treat not only cancer but also inflammatory and fibrosis-related diseases. The body uses DDR to repair damage to DNA in various ways. Oxcia’s projects make use if the fact that the diseased cells have altered DDR, with high levels of DNA damage and oxidative stress, to treat the disease.
| OXC-101 (Mitotic MTH1 inhibitor) | OXC-201 (OGG1 Inhibitor) | |
|---|---|---|
| What? | Treating cancer by taking advantage of the high load of endogenous DNA damage and oxidative stress in cancer cells. | Treating diseases caused by inflammation and fibrosis, e.g. pulmonary fibrosis, via DNA damage response pathways. |
| Problem today? | Cancers are heterogenous both between cancer indications and within same indication. Resistance development. Poor tolerability. | Treatment for these diseases are unsatisfactory. Risk for major loss of organ function, increased mortality and high costs for society. |
| Oxcia’s solution | OXC-101 ensures that cancer cells cannot repair the DNA and oxygen damage, so the cancer cell cannot grow and subsequently dies. | OGG1 inhibitor stops the inflammatory response as well as the fibrosis production and hence the disease. |
| Benefits | Targets cancer cell phenotype, rather than oncogene or tumour suppressor gene. Healthy cells are not affected. Makes cold tumours hot. Low resistance development. | Potential to cure the disease, not only addressing the symptoms. |